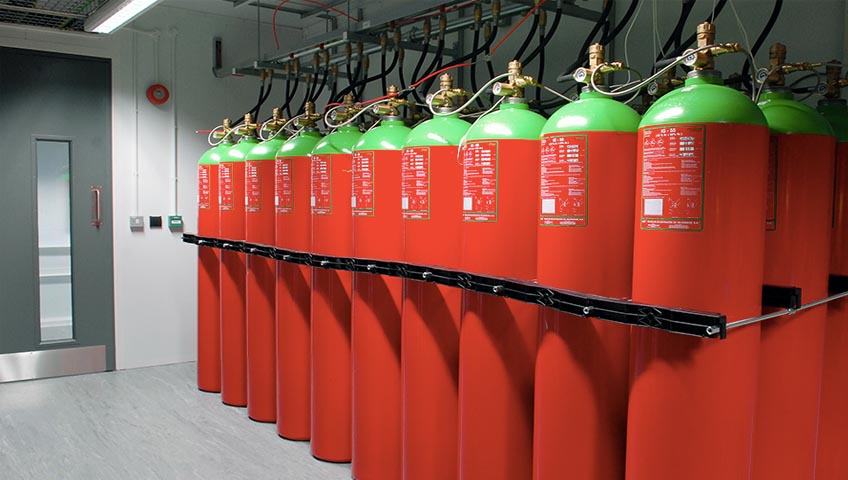
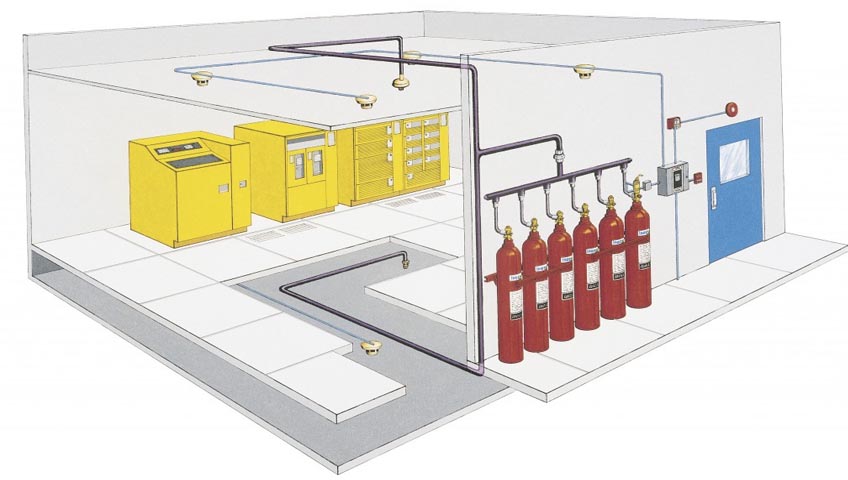
Automatic fire suppression systems control and extinguish fires without human intervention. Examples of automatic systems include fire sprinkler system, gaseous fire suppression, and condensed aerosol fire suppression.
Today there are numerous types of Automatic Fire Suppression Systems and standards for each one. Systems are as diverse as the many applications. In general, however, Automatic Fire Suppression Systems fall into two categories: engineered and pre-engineered systems. Engineered Fire Suppression Systems are design specific and most commonly used for larger installations where the system is designed for a particular application. Examples include large marine and land vehicle applications, server rooms, public and private buildings, industrial paint lines, dip tanks and electrical switch rooms. Engineered systems use a number of gaseous or solid agents with many of them being specifically formulated. Some are even stored as a liquid and discharged as a gas.
Pre-Engineered Fire Suppression Systems use pre-designed elements to eliminate the need for engineering work beyond the original product design. Typical industrial solutions use a wet or dry chemical agent, such as potassium carbonate or monoammonium phosphate (MAP), to protect relatively smaller spaces such as distribution boards, battery rooms, engine bays, wind turbines, hazardous goods and other storage areas. A number of residential designs have also emerged that typically employ water mist and target retrofit applications.